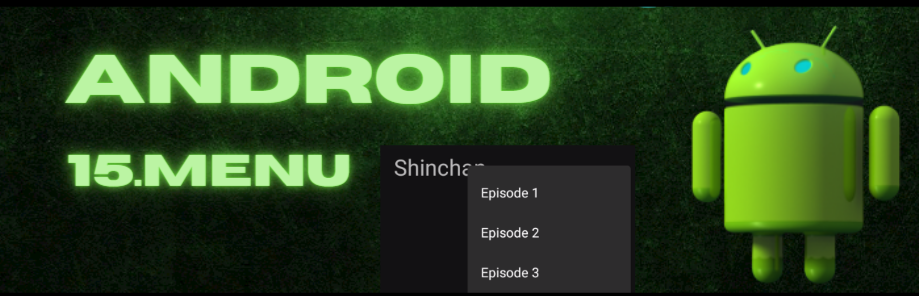
Android Menus
In designing Android apps, options menus play a significant role as they provide users with an easy way to access important actions. Whether you’re developing a productivity app or a social media platform,.This blog post covers their implementation, customization, and best practices.
Table of Contents
Types of Android Menus
Options Menu (Overflow Menu)/Action Bar menu
The options menu, also known as the overflow menu, is a standard menu that provides users with access to essential actions related to the current activity. It typically appears as three vertically stacked dots (also called the “hamburger” or “kebab” icon) in the top-right corner of the app’s action bar. The options menu is used for actions that don’t require frequent access and helps keep the UI clean and uncluttered.
Contextual Menus
A context menu is a floating menu that appears when a user long-presses on a UI element, such as a view or a list item. It provides context-specific actions related to the selected item. Context menus are useful for offering a set of relevant actions based on the user’s interaction with the app.
Popup Menu
A popup menu is a more flexible and customizable version of the context menu. It can be triggered by a click event and can appear anywhere on the screen, not necessarily near the triggering element. Popup menus are often used in scenarios where you want to provide options that are relevant to a specific area of the screen.
Options Menu
Options menus provide a context-specific list of actions that users can perform within an app. They are typically displayed when the user taps the “Menu” button or the three-dot “More” button on the screen.

Implementation
In your activity’s layout XML file, ensure that you have a Toolbar element or an ActionBar to host the options menu.
To see Status bar and Action bar in layout editor click on eye icon and select Show System UI.
1.Creating the Options Menu
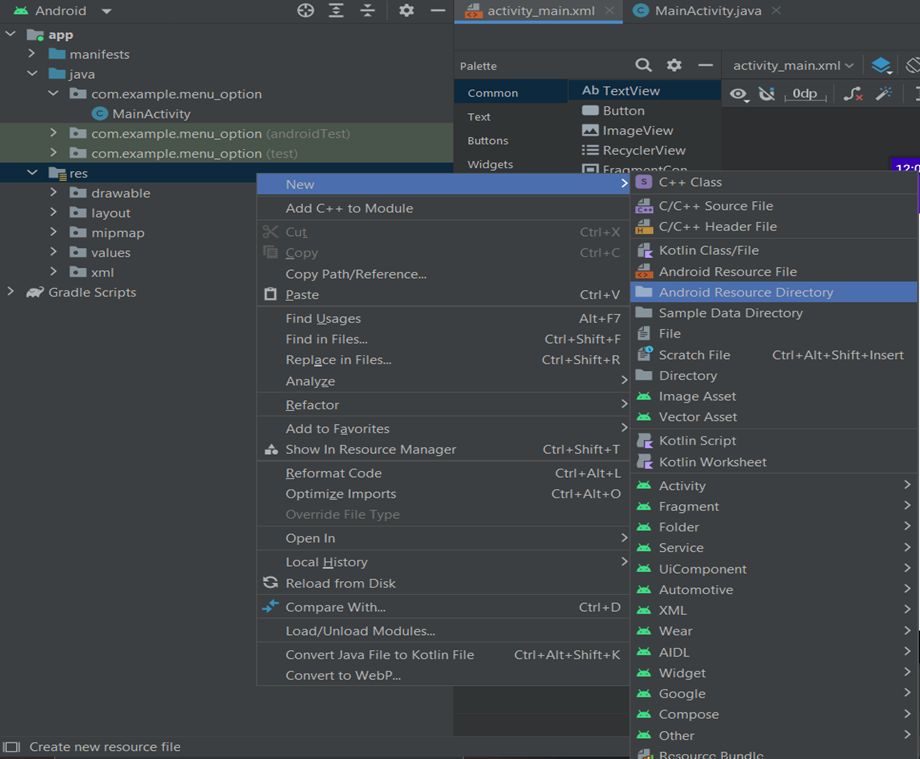
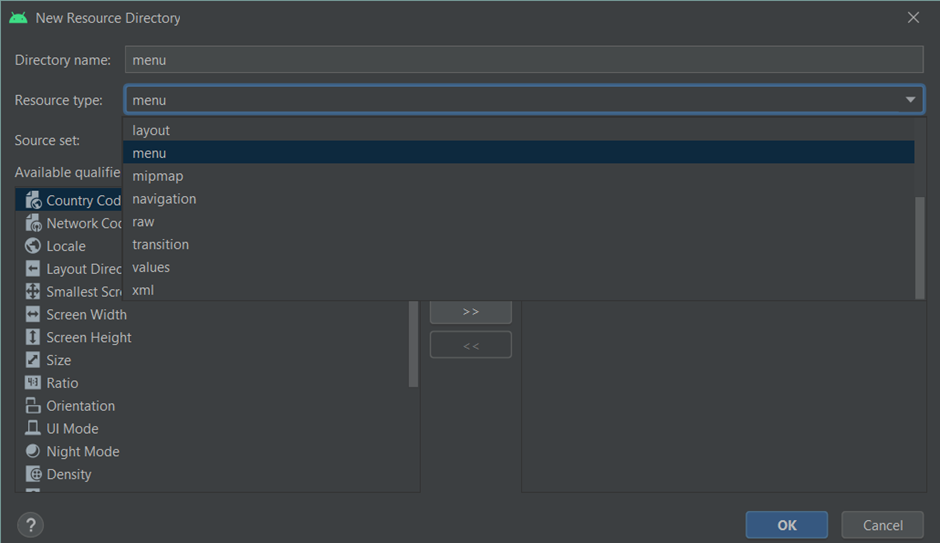
To create menu folder (android resource directory) right click on res folder and goto new->Android Resource Directory
select resource type as menu.
Right click on menu folder and create new menu resource file.
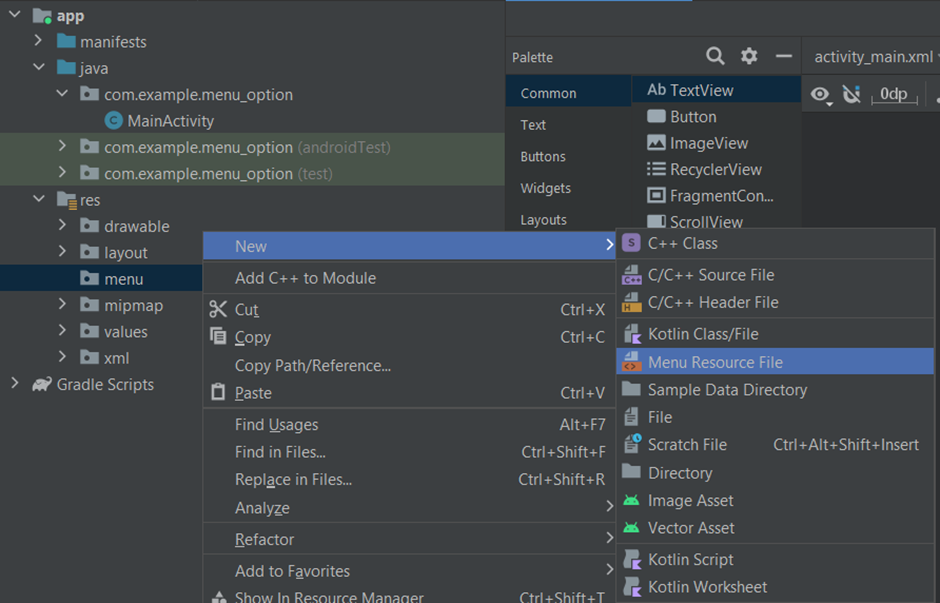
2.Adding Menu Items
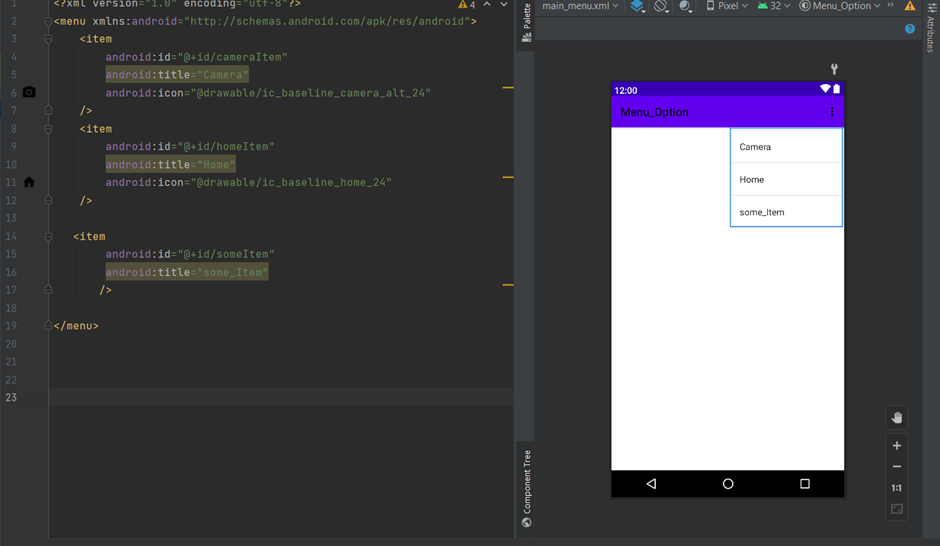
Define menu items using the element and provide icons, titles, and other attributes.
To list various items while clicking on the three dots you need go to app> res> menu> main_menu.xml and write down the code as shown in the highlighted area in the following screenshot:
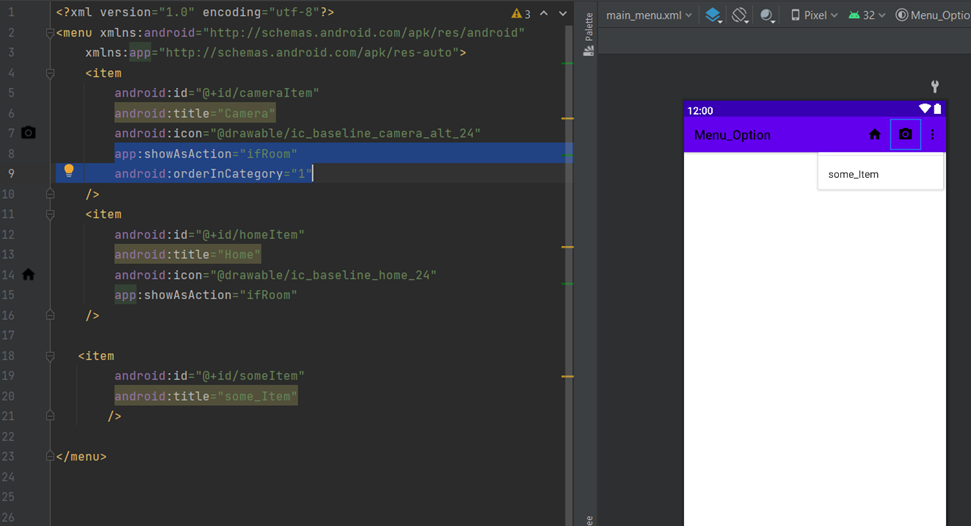
3.Attributes of items
On app items icon not visible its only visible on action bar to show icon of the item used attribute app:ashowAsAction=”ifRoom”.
android:showAsAction is used to specify how the item should appear as an action item in the app bar.
To order item on action bar use attribute android:orderInCategory by default order is zero(left side end icon is of order zero).
4.Adding Submenu(optional)
In case if we want to add submenu in menu item, then we need to add a <menu> element as the child of an <item>. As below,

5.Inflating the Options Menu
After adding menu override onCreateOPtionMenu method in MainActivity.and get inflate our menu by code as,
Kotlin:
override fun onCreateOptionsMenu(menu: Menu): Boolean {
val inflater: MenuInflater = menuInflater
inflater.inflate(R.menu.main_menu, menu)
return true
}Java:
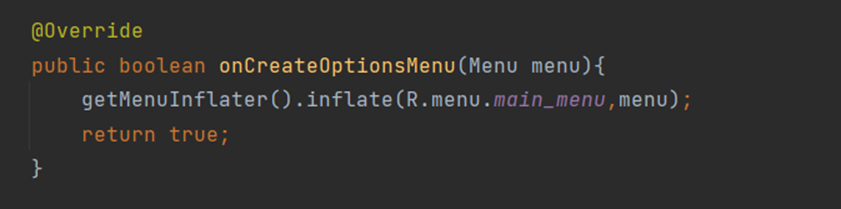
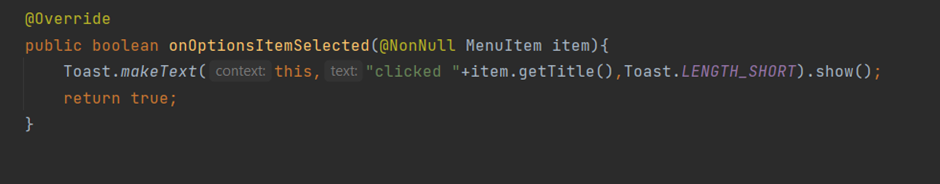
6.Handling Menu Item Selections
To handle the click of slelected item override the method onOptionsItemSelected().
Kotlin:
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean {
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return true
}MainActivity
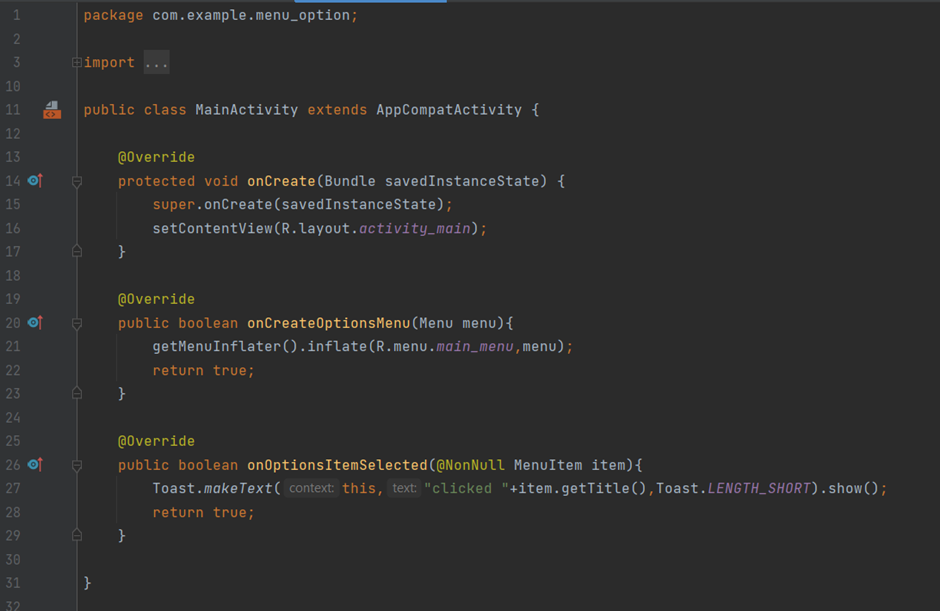
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
}
override fun onCreateOptionsMenu(menu: Menu): Boolean {
val inflater: MenuInflater = menuInflater
inflater.inflate(R.menu.main_menu, menu)
return true
}
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean {
Toast.makeText(this, "clicked", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return true
}
}
Java:
MainActivity
Contextual Menus
A contextual menu offers actions that affect a specific item or context frame in the UI. You can provide a context menu for any view, but they are most often used for items in a ListView, GridView, or other view collections in which the user can perform direct actions on each item.
There are two ways to provide contextual actions:
- In a floating context menu. A menu appears as a floating list of menu items (similar to a dialog) when the user performs a long-click (press and hold) on a view that declares support for a context menu. Users can perform a contextual action on one item at a time.
- In the contextual action mode. This mode is a system implementation of
ActionModethat displays a contextual action bar at the top of the screen with action items that affect the selected item(s). When this mode is active, users can perform an action on multiple items at once (if your app allows it).
Floating Context Menu

1.Register view
Register the View to which the context menu should be associated by calling registerForContextMenu() and pass it the View.
If your activity uses a ListView or GridView and you want each item to provide the same context menu, register all items for a context menu by passing the ListView or GridView to registerForContextMenu().
Kotlin:
val mListView = findViewById<ListView>(R.id.listview)
val adapter: ArrayAdapter<String> =
ArrayAdapter<Any?>(this, R.layout.simple_list_item_1, cartoons)
mListView.adapter = adapter
registerForContextMenu(mListView)
val txt = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.txt)
registerForContextMenu(txt)Java:
ListView mListView = findViewById(R.id.listview);
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, cartoons);
mListView.setAdapter(adapter);
registerForContextMenu(mListView);
TextView txt=findViewById(R.id.txt);
registerForContextMenu(txt);2.Implement the onCreateContextMenu()
When the registered view receives a long-click event, the system calls your onCreateContextMenu() method. This is where you define the menu items, usually by inflating a menu resource.
Kotlin:
override fun onCreateContextMenu(menu: ContextMenu?, v: View?, menuInfo: ContextMenuInfo?) {
super.onCreateContextMenu(menu, v, menuInfo)
menuInflater.inflate(R.menu.menu, menu)
}Java:
@Override
public void onCreateContextMenu(ContextMenu menu, View v, ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo menuInfo) {
super.onCreateContextMenu(menu, v, menuInfo);
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu,menu);
}3.Implement onContextItemSelected()
When the user selects a menu item, the system calls this method so you can perform the appropriate action.
Kotlin:
override fun onContextItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean {
Toast.makeText(this, "clicked" + item.title, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return super.onContextItemSelected(item)
}Java:
@Override
public boolean onContextItemSelected(@NonNull MenuItem item) {
Toast.makeText(this,"clicked"+item.getTitle(),Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return super.onContextItemSelected(item);
}
Contextual Action mode
Enabling the contextual action mode for individual views
If you want to invoke the contextual action mode only when the user selects specific views, you should.
1.Implement the ActionMode.Callback interface
Implement the ActionMode.Callback interface. In its callback methods, you can specify the actions for the contextual action bar, respond to click events on action items, and handle other lifecycle events for the action mode.
Kotlin:
private val actionModeCallback = object : ActionMode.Callback {
// Called when the action mode is created. startActionMode() is called.
override fun onCreateActionMode(mode: ActionMode, menu: Menu): Boolean {
// Inflate a menu resource providing context menu items.
val inflater: MenuInflater = mode.menuInflater
inflater.inflate(R.menu.context_menu, menu)
return true
}
// Called each time the action mode is shown. Always called after
// onCreateActionMode, and might be called multiple times if the mode
// is invalidated.
override fun onPrepareActionMode(mode: ActionMode, menu: Menu): Boolean {
return false // Return false if nothing is done
}
// Called when the user selects a contextual menu item.
override fun onActionItemClicked(mode: ActionMode, item: MenuItem): Boolean {
return when (item.itemId) {
R.id.menu_share -> {
shareCurrentItem()
mode.finish() // Action picked, so close the CAB.
true
}
else -> false
}
}
// Called when the user exits the action mode.
override fun onDestroyActionMode(mode: ActionMode) {
actionMode = null
}
}
Java:
private ActionMode.Callback actionModeCallback = new ActionMode.Callback() {
// Called when the action mode is created; startActionMode() was called
@Override
public boolean onCreateActionMode(ActionMode mode, Menu menu) {
// Inflate a menu resource providing context menu items
MenuInflater inflater = mode.getMenuInflater();
inflater.inflate(R.menu.context_menu, menu);
return true;
}
// Called each time the action mode is shown. Always called after onCreateActionMode, but
// may be called multiple times if the mode is invalidated.
@Override
public boolean onPrepareActionMode(ActionMode mode, Menu menu) {
return false; // Return false if nothing is done
}
// Called when the user selects a contextual menu item
@Override
public boolean onActionItemClicked(ActionMode mode, MenuItem item) {
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.menu_share:
shareCurrentItem();
mode.finish(); // Action picked, so close the CAB
return true;
default:
return false;
}
}
// Called when the user exits the action mode
@Override
public void onDestroyActionMode(ActionMode mode) {
actionMode = null;
}
};2.Call startActionMode() when you want to show the bar (such as when the user long-clicks the view)
Kotlin:
someView.setOnLongClickListener(OnLongClickListener { view ->
// Called when the user long-clicks on someView
if (actionMode != null) {
return@OnLongClickListener false
}
// Start the CAB using the ActionMode.Callback defined above
actionMode = getActivity().startActionMode(actionModeCallback)
view.isSelected = true
true
})Java:
someView.setOnLongClickListener(new View.OnLongClickListener() {
// Called when the user long-clicks on someView
public boolean onLongClick(View view) {
if (actionMode != null) {
return false;
}
// Start the CAB using the ActionMode.Callback defined above
actionMode = getActivity().startActionMode(actionModeCallback);
view.setSelected(true);
return true;
}
});Example:

Kotlin:
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private var actionMode: ActionMode? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val txt = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.txt)
txt.setOnLongClickListener { view: View ->
if (actionMode != null) {
return@setOnLongClickListener false
}
// Start the CAB using the ActionMode.Callback defined above
actionMode = startActionMode(actionModeCallback)
view.isSelected = true
true
}
}
private val actionModeCallback: ActionMode.Callback = object : Callback() {
// Called when the action mode is created; startActionMode() was called
fun onCreateActionMode(mode: ActionMode, menu: Menu?): Boolean {
// Inflate a menu resource providing context menu items
val inflater: MenuInflater = mode.getMenuInflater()
inflater.inflate(R.menu.menu, menu)
return true
}
// Called each time the action mode is shown. Always called after onCreateActionMode, but
// may be called multiple times if the mode is invalidated.
fun onPrepareActionMode(mode: ActionMode?, menu: Menu?): Boolean {
// Return false if nothing is done
return false
}
fun onActionItemClicked(mode: ActionMode?, item: MenuItem): Boolean {
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "clicked" + item.title, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return true
}
// Called when the user exits the action mode
fun onDestroyActionMode(mode: ActionMode?) {
actionMode = null
}
}
}Java:public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ActionMode actionMode;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView txt=findViewById(R.id.txt);
txt.setOnLongClickListener(view -> {
if (actionMode != null) {
return false;
}
// Start the CAB using the ActionMode.Callback defined above
actionMode = startActionMode(actionModeCallback);
view.setSelected(true);
return true;
});
}
private ActionMode.Callback actionModeCallback=new ActionMode.Callback() {
// Called when the action mode is created; startActionMode() was called
@Override
public boolean onCreateActionMode(ActionMode mode, Menu menu) {
// Inflate a menu resource providing context menu items
MenuInflater inflater = mode.getMenuInflater();
inflater.inflate(R.menu.menu, menu);
return true;
}
// Called each time the action mode is shown. Always called after onCreateActionMode, but
// may be called multiple times if the mode is invalidated.
@Override
public boolean onPrepareActionMode(ActionMode mode, Menu menu) {
// Return false if nothing is done
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onActionItemClicked(ActionMode mode, MenuItem item) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"clicked"+item.getTitle(),Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
// Called when the user exits the action mode
@Override
public void onDestroyActionMode(ActionMode mode) {
actionMode = null;
}
};
}Enabling batch contextual actions in a ListView or GridView
1.Implement the AbsListView.MultiChoiceModeListener interface and set it for the view group with setMultiChoiceModeListener(). In the listener’s callback methods, you can specify the actions for the contextual action bar, respond to click events on action items, and handle other callbacks inherited from the ActionMode.Callback interface.
2.Call setChoiceMode() with the CHOICE_MODE_MULTIPLE_MODAL argument.
Example:
Kotlin:
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val actionMode: ActionMode? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val cartoons = ArrayList<String>()
cartoons.add("Item 1")
cartoons.add("Item 2")
cartoons.add("Item 3")
val listView = findViewById<ListView>(R.id.listview)
val adapter = ArrayAdapter(this, R.layout.simple_list_item_1, cartoons)
listView.adapter = adapter
listView.choiceMode = ListView.CHOICE_MODE_MULTIPLE_MODAL
listView.setMultiChoiceModeListener(object : MultiChoiceModeListener {
override fun onCreateActionMode(mode: ActionMode, menu: Menu?): Boolean {
// Inflate the menu for the CAB
val inflater: MenuInflater = mode.getMenuInflater()
inflater.inflate(R.menu.menu, menu)
return true
}
override fun onPrepareActionMode(mode: ActionMode?, menu: Menu?): Boolean {
// Here you can perform updates to the CAB due to
// an <code><a href="/reference/android/view/ActionMode.html#invalidate()">invalidate()</a></
return false
}
override fun onActionItemClicked(mode: ActionMode?, item: MenuItem?): Boolean {
// Respond to clicks on the actions in the CAB
return false
}
override fun onDestroyActionMode(mode: ActionMode?) {
// Here you can make any necessary updates to the activity when
// the CAB is removed. By default, selected items are deselected/unchecked.
}
override fun onItemCheckedStateChanged(
mode: ActionMode?,
position: Int,
id: Long,
checked: Boolean
) {
// Here you can do something when items are selected/de-selected,
// such as update the title in the CAB
}
})
}
}Java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ActionMode actionMode;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ArrayList<String> cartoons = new ArrayList<>();
cartoons.add("Item 1");
cartoons.add("Item 2");
cartoons.add("Item 3");
ListView listView = findViewById(R.id.listview);
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, cartoons);
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
listView.setChoiceMode(ListView.CHOICE_MODE_MULTIPLE_MODAL);
listView.setMultiChoiceModeListener(new AbsListView.MultiChoiceModeListener() {
@Override
public boolean onCreateActionMode(ActionMode mode, Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu for the CAB
MenuInflater inflater = mode.getMenuInflater();
inflater.inflate(R.menu.menu, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onPrepareActionMode(ActionMode mode, Menu menu) {
// Here you can perform updates to the CAB due to
// an <code><a href="/reference/android/view/ActionMode.html#invalidate()">invalidate()</a></
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onActionItemClicked(ActionMode mode, MenuItem item) {
// Respond to clicks on the actions in the CAB
return false;
}
@Override
public void onDestroyActionMode(ActionMode mode) {
// Here you can make any necessary updates to the activity when
// the CAB is removed. By default, selected items are deselected/unchecked.
}
@Override
public void onItemCheckedStateChanged(ActionMode mode, int position, long id, boolean checked) {
// Here you can do something when items are selected/de-selected,
// such as update the title in the CAB
}
});
}
}Popup Menu
contextual menus are suitable for providing context-specific actions for selected items, often in the context of multi-selection, they are useful when you want to enable users to perform actions on multiple selected items simultaneously.
Example: In a messaging app, long pressing a message in the chat list might trigger a contextual menu with options to delete, mark as read, or reply to the selected message.
while popup menus are ideal for offering additional options or actions triggered by a click event on a specific UI element.
Example: In a messaging app, long pressing a message in the chat list might trigger a contextual menu with options to delete, mark as read, or reply to the selected message.
Implementation
If you define menu XML, here’s how you can show the popup menu:
- Instantiate a
PopupMenuwith its constructor, which takes the current applicationContextand theViewto which the menu should be anchored. - Use
MenuInflaterto inflate your menu resource into theMenuobject returned byPopupMenu.getMenu(). - Call
PopupMenu.show().

Kotlin:class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val popupButton = findViewById<Button>(R.id.btn)
popupButton.setOnClickListener { v -> showPopupMenu(v) }
}
private fun showPopupMenu(v: View) {
val popupMenu = PopupMenu(this, v)
val inflater: MenuInflater = popupMenu.getMenuInflater()
inflater.inflate(R.menu.menu, popupMenu.getMenu())
// Set a listener for menu item clicks
popupMenu.setOnMenuItemClickListener(object : OnMenuItemClickListener() {
fun onMenuItemClick(item: MenuItem): Boolean {
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Clicked" + item.title, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return true
}
})
popupMenu.show()
}
}Java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button popupButton=findViewById(R.id.btn);
popupButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showPopupMenu(v);
}
});
}
private void showPopupMenu(View v) {
PopupMenu popupMenu = new PopupMenu(this, v);
MenuInflater inflater = popupMenu.getMenuInflater();
inflater.inflate(R.menu.menu, popupMenu.getMenu());
// Set a listener for menu item clicks
popupMenu.setOnMenuItemClickListener(new PopupMenu.OnMenuItemClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onMenuItemClick(MenuItem item) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"Clicked"+item.getTitle(),Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
});
popupMenu.show();
}
}official android doc: Menus | Android Developers